Polyethylene (PE) is less expensive and thus a fairly widely used plastic. Its high chemical resistance to acids, alkalis and a variety of other chemicals is offset by its comparatively low thermal resistance.
At temperatures above 80°C, polyethylene begins to deform. Its resistance to ultraviolet radiation can be increased by adding carbon black.
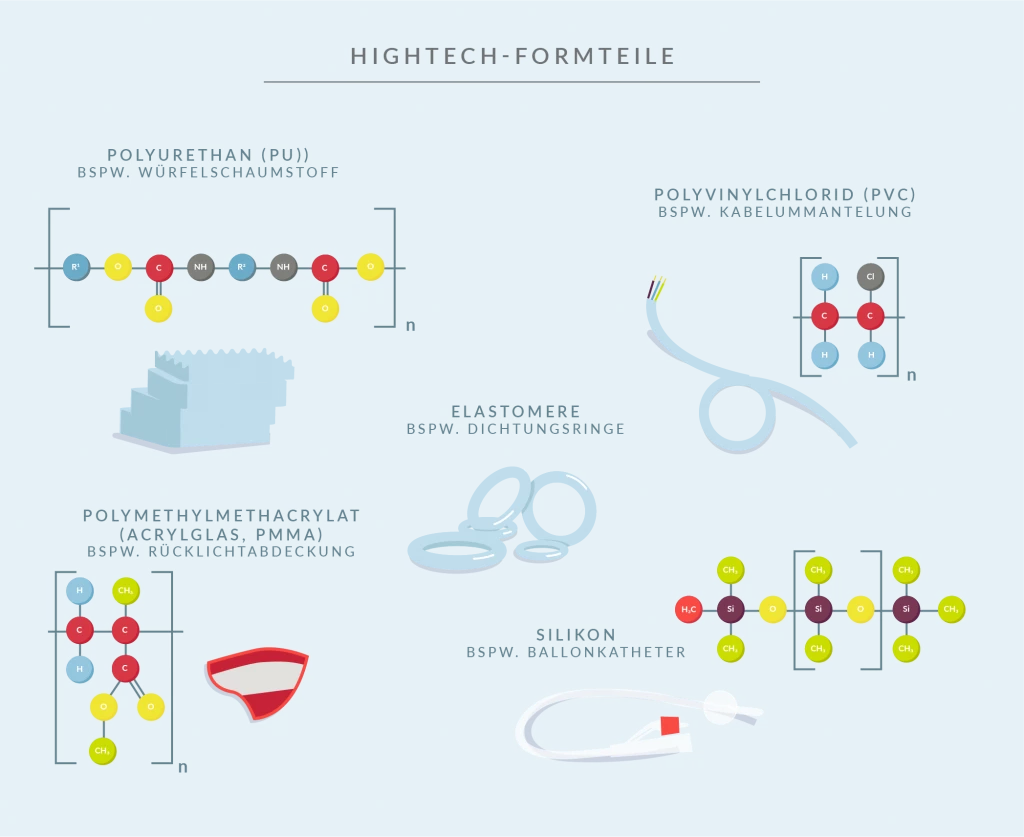
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a versatile thermoplastic that can be easily processed by injection molding. The elastic properties of PVC can be increased by adding plasticizers. Due to its low cost and high chemical resistance, PVC is used for flooring and cable sheathing, for example.
Molded parts made of PVC are characterized by a very high electrical insulation capacity.
Polyurethane (PU) is a plastic whose properties can be greatly varied during production by adding various additives. For example, flame retardants or plasticizers can be added to polyurethane to create molded parts for special applications.
Polyurethanes are very easy to produce dimensionally stable foams.
Polymethyl methacrylate (acrylic glass, PMMA) is a transparent, thermoplastic material that is extremely easy to process. PMMA moldings can be produced by injection molding, whereby the physical and mechanical properties of the molded part can be influenced by the type of production process.
The finished product is characterized by very high chemical resistance and insensitivity to many different substances and environmental influences. This makes acrylic a very popular plastic for molded part production.
Rubber is a generic term for various elastomers obtained from natural products by chemical treatment. As an example, natural rubber, which is given a very high abrasion resistance by vulcanization. Molded parts made of rubber are generally characterized by very favorable prices.
Foam is also a collective term for various plastics that are suitable for the production of molded parts. Foams are characterized by a low density and, due to their cellular structure, by a high thermal insulation effect.